- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Overview
Corezoid API operates in the asynchronous mode when requesting a new task creation in a Corezoid process. This means that in the response you receive a task ID, not the process output it invokes:
{
"request_proc": "ok",
"ops": [
{
"id": "",
"proc": "ok",
"obj": "task",
"ref": "ref",
"obj_id": "5d1b6ee5f6c37653b9904f7d"
}
]
}
For example, you need to implement the logic of P2P money transfer from client A to client B on a website that consists of:
- JS front-end without business logic.
- Corezoid back-end that manages the business logic.
If you use the Corezoid API to send tasks to a Corezoid process, you receive obj_id (Task ID) but not the requested process output, preventing you from developing the JS front-end.
To receive a task-invoked process output, you must implement the synchronous response.
By processing requests synchronously and using the Sync API module, you can receive requested outputs from Processes by sending requests via the Corezoid Sync API. Thus, Sync API serves the same purpose as the API Gateway.
 Use our collection of Corezoid Sync API queries for Postman as an example
Use our collection of Corezoid Sync API queries for Postman as an exampleSync API protocol
The Sync API protocol is compatible with the API Gateway protocol. For the Sync API protocol, the following task format is used:
{
"__callback_url": "https://url...",
"__headers": {
"user-agent": "curl/7.87.0"
},
"incKey": 12345
}
Things to keep in mind when using Sync API
When sending a request via Sync API, the
__callback_urlsystem parameter is automatically included in the task. This parameter keeps a link to a caller service, to which Corezoid should respond:"__callback_url": "https://sync-api.corezoid.com/api/1/plugins/callback/{{request_id}}"To configure a synchronous response, you need to:
- Add the API Call node to the Process step, which should send a requested output to a caller service.
- Provide the
{{__callback_url}}. - Specify the parameters that will be sent to the caller service.
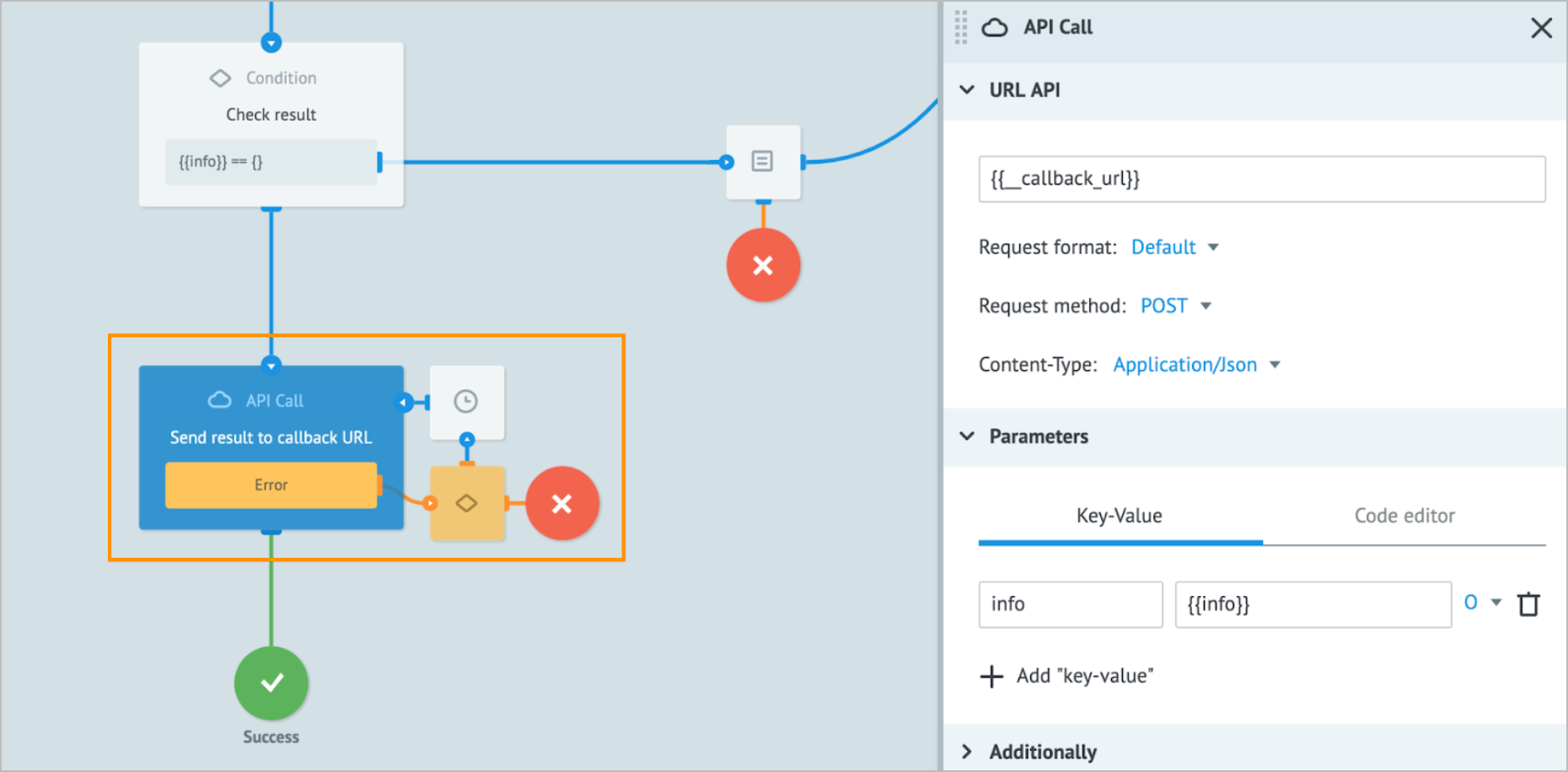
Thus, you can use Sync API in a way similar to Corezoid API.
Note: For more information on Corezoid API use, go to Corezoid API reference.Specify the
X-Status-Codekey in the Other->Header parameters of the Corezoid node from which the response is sent to the callback URL. This key allows for the specification of any status code within the 200 to 599 range in the Value field and returns it in the response.
Note: All headers are always sent.
Example
Below is an example of a task creation request to Sync API from an external service.
URL
https://sync-api.corezoid.com/api/1/json/{{API_LOGIN}}/{{TIMESTAMP}}/{{SIGNATURE}}
Where:
- {{API_LOGIN}}: Is the authorization login.
- {{GMT_UNIXTIME}}: Is the request time.
- {{SIGNATURE}}: Is the request signature.
- Request time should be in the Unix time format: number of seconds elapsed from the Unix epoch at the GMT+0 Time Zone.
- A mandatory request signature is created according to the standard Corezoid API protocol.
- You need to grant access to Task management to an API key, which login and password are used in the request.
Task creation request
{
"timeout": 30,
"ops": [{
"conv_id": {{CONV_ID}},
"type": "create",
"obj": "task",
"data": {
"param": 1
}
}]
}
| Parameter | Accept type | Description | Required | Possible value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ops | JSON Object | The list of operations to proceed via Corezoid API. A parameter keeping JSON objects with operations. | + | The number is user-limited by RPS limit. Note: Go to the License attributes. |
| type | string | A type for creating a task. | + | create |
| conv_id | number / number as string | An ID of a Process for which the task is created. | + | An ID of an existing Process. |
| obj | string | An object type. | + | task |
| data | JSON Object | An object with key-value pairs describing necessary parameters. | + | ** The quantity of parameters is not limited. Note: A task is limited to a size specified in a configuration file. |
| timeout | number | The maximum time of waiting for the response. | - | The number of seconds; the default value is 60 seconds. |
Successful response
{
"ops": [
{
"proc": "ok",
"data": {
"info": {
"param_1": "value_1",
"param_2": "value_2",
"param_3": "value_3"
}
}
}
],
"request_proc": "ok"
}
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request_proc | It is ok for the successful accomplishment or error otherwise. | The global processing status of the whole package. |
| ops | [] | A list of operations as requested. |
| ops[n].proc | It is ok for the successful accomplishment or error otherwise. | Processing status of a given operation. |
| data | An object with key-value pairs describing necessary parameters. | Data specified for response in the API Call node. |
To see examples of creating tasks by Alias with Sync API, go to the Postman queries collection.
Error examples
As Sync API works with APIs, it mostly returns errors similar to Corezoid API. However, there are some Sync API-specific errors that you can see in the examples below.
Response to a request from an API key with an incorrect signature
{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "Bad signature" } ] }Response to an incorrect body request (code 400)
{ "request_proc":"ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "Incorrect body" } ] }Response was not received in the specified period (code 200)
The
timeoutparameter allows setting the period for response waiting. In case the response was not received in the period specified, the following error is generated:{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "Timeout for create task" } ] }Request limit for a user is exceeded
The following errors are proxied from CAPI and have the 200 code and N is the limit set for requests sent in a process for the process owner.{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "too many requests, you exceeded user limit N/sec" } ] }
Examples of validation and integrity check errors
Conveyor is not active.
{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "conveyor is not active" } ] }Non-unique REF parameter value.
{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "not_unical_ref" } ] }Access for api_copy is denied.
{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "access_denied" } ] }Conveyor was not found.
{ "request_proc": "ok", "ops": [ { "proc": "error", "description": "conveyor not found" } ] }


